Local Social Inequity Score Offers Precise Analysis of Social Risk Data
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently released guidance that outlines specific diversity requirements sponsors must submit for clinical studies involving drugs, devices, and biological products. Sponsors will need to identify potential obstacles to enrollment, such as geographic disparities and socioeconomic factors, and to develop Diversity Action Plans (DAPs) to overcome these challenges. Compliance with these guidelines will be mandatory for clinical trials beginning enrollment starting at 180 days after the final guidance is published.
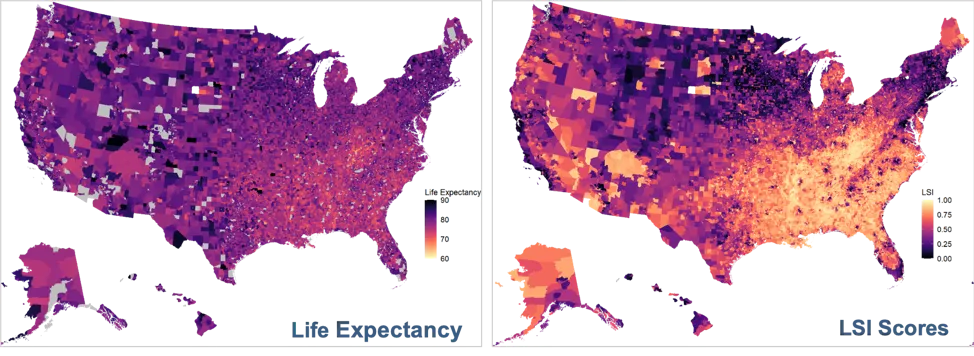
What is the RTI Rarity Local Social Inequity score?
The RTI Rarity tool merges artificial intelligence, advanced data science methods, and geospatial analytics in a risk adjustment framework. Featuring a supervised machine learning method known as random forests and other state-of-the-art predictive analytics methods, RTI Rarity generates a Local Social Inequity (LSI) score that provides meaningful insights into the social determinants of health (SDoH) affecting local health outcomes.
What data does the RTI Rarity LSI score leverage?
RTI Rarity creates and delivers the LSI score by drawing on 40+ public and private datasets from publicly available federal, state, non-profit, and academic resources, including:
- US Census Bureau's American Community Survey (ACS)
- USDA's Food Environment Atlas
- CDC's Wide-ranging ONline Data for Epidemiologic Research (WONDER)
- Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Child Opportunity Index (COI)
- Opportunity Atlas
- and 34+ other datasets
The RTI Rarity LSI score uses 200+ area-level variables across 10 domains at the Census, zip code, and county levels for predicting life expectancy and other health outcomes to provide sponsors with comprehensive SDoH and health equity data they need to comply with the new FDA requirements.